
4.1 Understanding Sexual
and Asexual Reproduction
![]() Process
that take place in living organisms in order to perpetuate their respective
species
Process
that take place in living organisms in order to perpetuate their respective
species
![]() Process
of producing now individuals from living organisms
Process
of producing now individuals from living organisms
![]() Process
of generating offspring
Process
of generating offspring
![]() Biologically
process that occurs in all living organisms
Biologically
process that occurs in all living organisms
Importance of reproduction
![]() The way
to increase the number of individual or offspring of the same species.
The way
to increase the number of individual or offspring of the same species.
![]() Importance
for the survival of all living organisms
Importance
for the survival of all living organisms
![]() Importance
to maintaining continuity of organisms without a mechanisms for reproduction,
life would come to end
Importance
to maintaining continuity of organisms without a mechanisms for reproduction,
life would come to end
Fertilization
![]() Fertilization
is a fusion process between a male gamete and a female gamete to produce a
zygote.
Fertilization
is a fusion process between a male gamete and a female gamete to produce a
zygote.
![]() The are
two types of fertilization :
The are
two types of fertilization :
a) internal
fertilization
b) external
fertilization
![]() The
internal fertilization takes place in the body of the female animal. The male
animal puts the male reproductive cell into the female reproductive system for
fertilization to take place.
The
internal fertilization takes place in the body of the female animal. The male
animal puts the male reproductive cell into the female reproductive system for
fertilization to take place.
![]() The
external fertilization takes place outside the body of the female animal. Ovum
and sperm are produced respectively by the female and male animal at the same
time into water for the fertilization to take place.
The
external fertilization takes place outside the body of the female animal. Ovum
and sperm are produced respectively by the female and male animal at the same
time into water for the fertilization to take place.
![]() The
internal fertilization take place in mammals,
reptiles, birds and insects.
The
internal fertilization take place in mammals,
reptiles, birds and insects.
![]() The
external fertilization takes place in fish, frogs and toads.
The
external fertilization takes place in fish, frogs and toads.
![]() Disadvantage
of external fertilization:
Disadvantage
of external fertilization:
a) a lot of reproductive cells need to be produced
b) a lot of reproductive cells diet before fertilization
occurs
c) a lot of
ovum and sperms are wasted, as they are
washed away by water
d) the
zygote or embryo produced may be eaten by other animals
![]() Reproduction
are divide by two :
Reproduction
are divide by two :
- Sexual reproduction
- Asexual reproduction
Sexual Reproduction
![]() Production
of new individuals by the living organisms
Production
of new individuals by the living organisms
![]() Sex
cells called gametes
Sex
cells called gametes
![]() Process
of producing a new individuals through the fusion of
one male reproductive cell (female gamete) to produce zygote. Zygote will
develop to form a new individual.
Process
of producing a new individuals through the fusion of
one male reproductive cell (female gamete) to produce zygote. Zygote will
develop to form a new individual.
![]() Organisms
that carry out sexual reproduction include
Organisms
that carry out sexual reproduction include
a) human
b) all vertebrate
animals
c) insects
d) most flowering
plants
Asexual reproduction
![]() Production
of new individuals by living organisms without involving sex cells
Production
of new individuals by living organisms without involving sex cells
![]() Involves
one individual organisms
Involves
one individual organisms
![]() Does
not involve the fusion of male and female sex cells.
Does
not involve the fusion of male and female sex cells.
![]() No
gamete involves
No
gamete involves
![]() A
simple cell is divided by itself to produce an exact duplicate of an organisms.
A
simple cell is divided by itself to produce an exact duplicate of an organisms.
![]() There
are 5 types of asexual reproduction: binary fusion, budding, spore formation,
vegetative reproduction and rejuvenation
There
are 5 types of asexual reproduction: binary fusion, budding, spore formation,
vegetative reproduction and rejuvenation
![]() Organisms
that produce asexual are :
Organisms
that produce asexual are :
a) paramecium
b) hydra
c) amoeba
d) flowering
and non-flowering
4.2
Male Reproduction System
![]() The
male reproductive system functions to produce male gametes which are called
sperms.
The
male reproductive system functions to produce male gametes which are called
sperms.
![]() The
main male reproductive organs include :
The
main male reproductive organs include :
a) Testis
b) Penis
c) Scrotum
d) Urethra
e) Sperm duct
f) Prostate gland
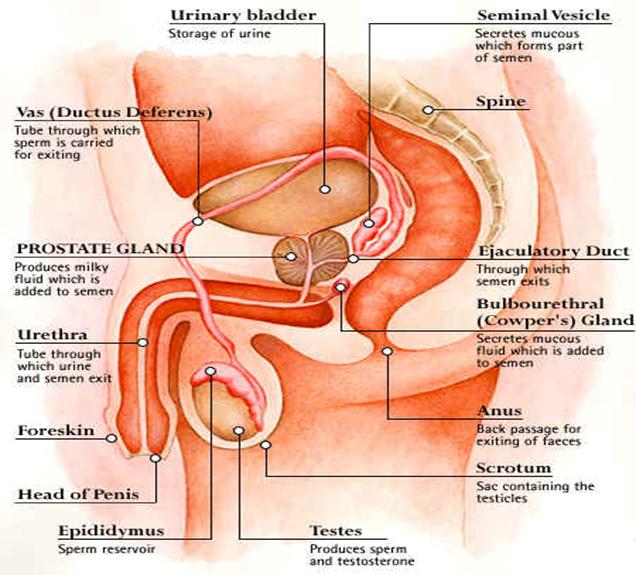
Figure
1: Male reproductive organs
|
Part |
Description
and function |
|
Sex
glands |
-
These include the seminal vesicle and prostate gland. Sex glands secrete
fluid which contains nutrients for the sperm. |
|
Sperm
duct |
-
A tube which transports sperms from the testis to the urethra inside the
body. |
|
Scrotum |
-
A sac which
hangs outside the body -
It holds and protects the testes |
|
Urethra |
-
A tube that runs through the penis -
It is a passage that allows sperm to flow
out of the body -
It is a passage that allows urine from the
bladder to be
excreted to the outside of the body. |
|
Penis |
-
Male sex organ which is made up of soft
tissues and rich with blood vessels -
It transfers semen into the vagina of the
female during copulation |
|
Testis |
-
Produces the male gametes (sperm) and male sex hormones |
Table 1 :
Functions of the male reproductive organs
SPERM
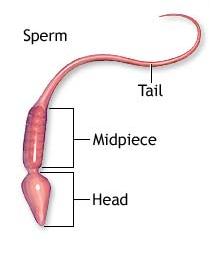
Figure
2 : Structure of the sperm
![]() The
sperm is the smallest cell in the male body.
It can move or swim on its own by moving its tail in the fluid.
The
sperm is the smallest cell in the male body.
It can move or swim on its own by moving its tail in the fluid.
![]() Each
sperm has three sections; head, neck and tail.
Each
sperm has three sections; head, neck and tail.
![]() The
sperm nucleus contains heredity substances that can be passed on to the next
generation.
The
sperm nucleus contains heredity substances that can be passed on to the next
generation.
Changes in males during
puberty
![]() Puberty
is the early stage of maturity in a person from a physical and spiritual
perspective.
Puberty
is the early stage of maturity in a person from a physical and spiritual
perspective.
![]() At the
puberty, the male will experience physical, physiological (body functions) and
emotional changes.
At the
puberty, the male will experience physical, physiological (body functions) and
emotional changes.
![]() A male
reaches puberty when he is about 12 to 14 years of age.
A male
reaches puberty when he is about 12 to 14 years of age.
![]() At
puberty, a male will experience the following changes:
At
puberty, a male will experience the following changes:
a) growth of
moustache and beard
b) enlargement of
bones and muscles
c) growth of pubic
and armpit hair
d) voice becomes
hoarse
e) testis begins
to produce sperm
f) begins to
release semen
g) begins to show
interest in female
4.3
Female reproductive system
![]() The
female reproductive system functions to produce female gametes called ovum.
The
female reproductive system functions to produce female gametes called ovum.
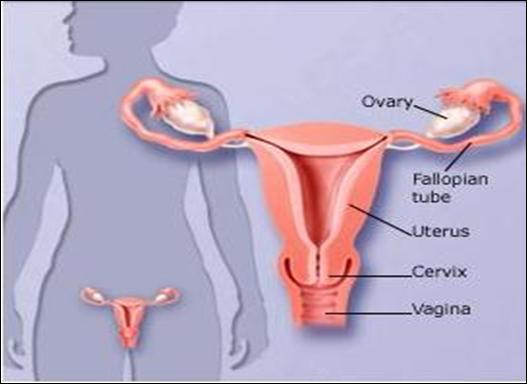
![]() The
main female reproductive organs include :
The
main female reproductive organs include :
a) ovary
b)
uterus
c)
Fallopian tube
d)
Vagina
e)
Cervix
![]() The
oviduct is a narrow vessel that joins the ovary with the uterus. The Fallopian
tube is the first part of the oviduct. Fertilization occurs here.
The
oviduct is a narrow vessel that joins the ovary with the uterus. The Fallopian
tube is the first part of the oviduct. Fertilization occurs here.
Figure
3 : Female reproductive organs
|
Reproductive |
Function |
|
Ovary |
-
Produces ovum |
|
Fallopian
tube |
-
Channels
ovum from the ovary to the uterus -
A place
where fertilization occurs |
|
Uterus |
-Accommodates
and protects the embryo |
|
Cervix |
-Connects
the uterus with the vagina -Produces
mucus for sperm movement |
|
Vagina |
-Receives
sperms from the penis -Produces
mucus for sperm movement |
Table
2 : Functions of the female reproductive.
Ovum
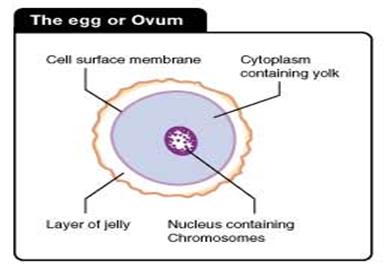
![]() The ovum
is the largest cell in the female body. It cannot move by itself.
The ovum
is the largest cell in the female body. It cannot move by itself.
![]() The
ovum contains nucleus, cytoplasm and a thick cell membrane.
The
ovum contains nucleus, cytoplasm and a thick cell membrane.
![]() The
nucleus of an ovum contains heredity substance like in the sperm nucleus.
The
nucleus of an ovum contains heredity substance like in the sperm nucleus.
![]() The
ovum cytoplasm provides food for the development of the zygote.
The
ovum cytoplasm provides food for the development of the zygote.
Figure
4 : Structure of ovum
Changes in the female during puberty
![]() At
puberty, the female will experience physical, physiological (body functions)
and emotional changes just like the male.
At
puberty, the female will experience physical, physiological (body functions)
and emotional changes just like the male.
![]() Puberty
for the female happens when she is about 9 to 12 years of age.
Puberty
for the female happens when she is about 9 to 12 years of age.
![]() At the
puberty, the female will experience the following changes:
At the
puberty, the female will experience the following changes:
a) enlargement of breast and buttocks
b)
accumulation of fats under the skin
c)
growth of pubic and armpit hair
d) begins to
produce ovum
e)
begins to menstruate
f)
begins to show interest in male
4.4
Menstrual Cycle
![]() Menstruation
is the bleeding or blood
discharge through the cervix and vagina of the female.
Menstruation
is the bleeding or blood
discharge through the cervix and vagina of the female.
![]() The
menstrual discharge contains blood, dead ovum and a layer of tissue which
covered the surface of the uterus wall.
The
menstrual discharge contains blood, dead ovum and a layer of tissue which
covered the surface of the uterus wall.
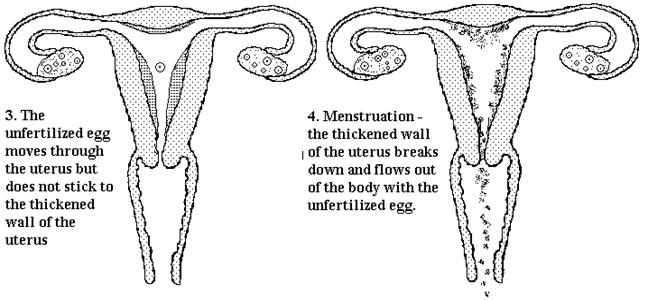
![]() During
the menstrual cycle, an ovum develops and is released. The uterus is
prepared for fertilization. If the ovum is not fertilized, the ovum, together
with the uterus wall tissues and blood is eliminated from the body as menstrual
discharge.
During
the menstrual cycle, an ovum develops and is released. The uterus is
prepared for fertilization. If the ovum is not fertilized, the ovum, together
with the uterus wall tissues and blood is eliminated from the body as menstrual
discharge.
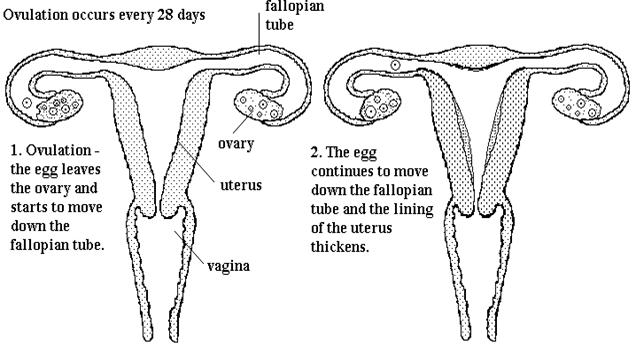
![]() About
every 28 days, an ovum will be released by one ovary and will enter the
Fallopian tube. The process of releasing ovum from the ovary is called ovulation.
About
every 28 days, an ovum will be released by one ovary and will enter the
Fallopian tube. The process of releasing ovum from the ovary is called ovulation.
![]() If an
ovum is fertilized by a sperm, a zygote will form and develop into an embryo
which will implant itself to the uterus wall. The woman is then said to be
pregnant and her menstrual cycle will stop until the baby is born.
If an
ovum is fertilized by a sperm, a zygote will form and develop into an embryo
which will implant itself to the uterus wall. The woman is then said to be
pregnant and her menstrual cycle will stop until the baby is born.
![]() If the
ovum is not fertilized, it will die after 24-36 hours. The tissue layer on the
thick and soft uterus wall will break off and be expelled together with blood
through the vagina are menstrual discharge.
If the
ovum is not fertilized, it will die after 24-36 hours. The tissue layer on the
thick and soft uterus wall will break off and be expelled together with blood
through the vagina are menstrual discharge.
![]() The
fertile phase is the period when ovulation is most likely to happen.
The
fertile phase is the period when ovulation is most likely to happen.
Human
menstrual cycle
Figure
5 : The menstrual cycle
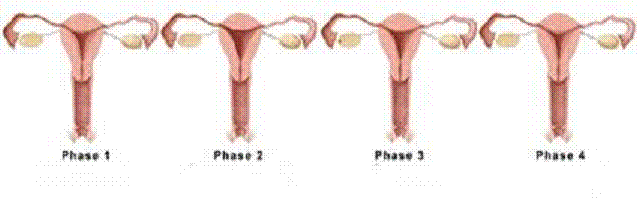
Figure
6 : Menstrual cycle and the fertile phase
![]() Phase 1
: Menstruation phase – 1st to 5th day
Phase 1
: Menstruation phase – 1st to 5th day
![]() Phase 2
: Repair phase – 6th to 11th day
Phase 2
: Repair phase – 6th to 11th day
![]() Phase 3
: Fertile phase or ovulation phase – 12th to 16th day
Phase 3
: Fertile phase or ovulation phase – 12th to 16th day
![]() Phase 4
: Premenstrual phase – 17th to 28th day
Phase 4
: Premenstrual phase – 17th to 28th day
![]() The
fertile phase is between the 11th and 17th day, in that day, the fertilization
can occur. This period is called the fertile phase.
The
fertile phase is between the 11th and 17th day, in that day, the fertilization
can occur. This period is called the fertile phase.
![]() An ovum
in a female body can live for 24 to 36 hours only. Because the ovum will be
released in the middle of the menstrual cycle; about the 14th day, this means
that fertilization can occur between the 11th and 17th day to produce a zygote
if the sperm enters the Fallopian tube.
An ovum
in a female body can live for 24 to 36 hours only. Because the ovum will be
released in the middle of the menstrual cycle; about the 14th day, this means
that fertilization can occur between the 11th and 17th day to produce a zygote
if the sperm enters the Fallopian tube.
![]() A
female must take care of her personal hygiene during the menstrual period and
carry out daily activities as usual.
A
female must take care of her personal hygiene during the menstrual period and
carry out daily activities as usual.
![]() When
menstruation begins, a female should :
When
menstruation begins, a female should :
a) wear a clean
sanitary pad
b) change the
sanitary pad frequently
c) bath as usual
to maintain body cleanliness
d) wrap used
sanitary pads with a paper or plastic bag before throwing it into a closed
rubbish
bin.
Fertilization
and Pregnancy
![]() Fertilization
is a process whereby the sperm fuses with the ovum to form the zygote.
Fertilization
is a process whereby the sperm fuses with the ovum to form the zygote.
![]() During
copulation, millions of sperms are transferred into the vagina.
During
copulation, millions of sperms are transferred into the vagina.
![]() From
the vagina, the sperms swim through the cervix into the uterus and up the
oviduct to meet the ovum.
From
the vagina, the sperms swim through the cervix into the uterus and up the
oviduct to meet the ovum.
![]() If the
ovum is present in the oviduct, fertilization takes place.
If the
ovum is present in the oviduct, fertilization takes place.
![]() During
ovulation, a mature ovum is released.
During
ovulation, a mature ovum is released.
![]() The
ovum moves along the fallopian tube or oviduct towards the uterus.
The
ovum moves along the fallopian tube or oviduct towards the uterus.
![]()
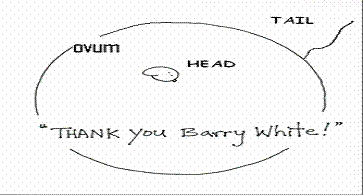
 Millions
of sperms are released during the copulation. However, only about 100 will
reach the ovum but only 1 is able to fuse with the ovum.
Millions
of sperms are released during the copulation. However, only about 100 will
reach the ovum but only 1 is able to fuse with the ovum.
![]() The
fusion between the sperm and the ovum is called fertilization.
The
fusion between the sperm and the ovum is called fertilization.
![]() Fertilization
produces a zygote.
Fertilization
produces a zygote.
![]() The
zygote divides in 2, then 4, and so on.
The
zygote divides in 2, then 4, and so on.
![]() After
six days, a ball of cells, now called an embryo, is formed.
After
six days, a ball of cells, now called an embryo, is formed.
![]() When
implantation is successful, the woman is said to be pregnant.
When
implantation is successful, the woman is said to be pregnant.
![]() It
takes 9 month from the time the zygote is formed until the fetus is ready to be
born.
It
takes 9 month from the time the zygote is formed until the fetus is ready to be
born.
Figure
7 : Fertilization of an ovum by a sperm
Development
of the embryo into a fetus until birth.
![]() The embryo, which subsequently becomes the foetus,
grows inside the uterus in a sac surrounded by a membrane called amnion.
The embryo, which subsequently becomes the foetus,
grows inside the uterus in a sac surrounded by a membrane called amnion.
![]() A flexible tube called umbilical cord connects the
embryo to the placenta.
A flexible tube called umbilical cord connects the
embryo to the placenta.
|
|
- Place where embryo implants itself and
develops. - Has muscular walls. |
|
|
- Made up of tissue from both mother and the fetus. - Place where exchange of nutrients, oxygen,
carbon dioxide and waste materials takes place between the blood of the
mother and the fetus |
|
|
- Tube which connects the fetus to the
placenta. - Inside the tube are blood vessels to
transport blood to and from the fetus. |
|
|
- Membrane which forms a sac and contains
fluid. |
|
|
- Forms from an embryo. |
|
|
- Acts as a cushion and absorb shock. |
HUMAN
LIFECYCLE
2.Embryo

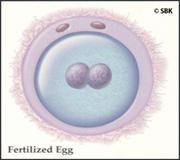
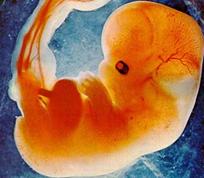
4. Fetus with all the parts fully formed
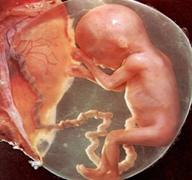

![]() After
about 9 months, the fetus is fully formed and ready to be born
After
about 9 months, the fetus is fully formed and ready to be born
![]() The
fetus rotates its body until the head points towards the cervix which dilates,
and makes the mother goes into labors.
The
fetus rotates its body until the head points towards the cervix which dilates,
and makes the mother goes into labors.
![]() During
labor, the muscular wall of the uterus contracts, the amnion bursts and
amniotic fluid is released.
During
labor, the muscular wall of the uterus contracts, the amnion bursts and
amniotic fluid is released.
![]() The
fetus is pushed out through the vagina, the baby is born and the umbilical cord
is cut.
The
fetus is pushed out through the vagina, the baby is born and the umbilical cord
is cut.
THE
IMPORTANCE OF PRE-NATAL CARE
![]() Throughout
the pregnancy, the fetus obtains food supply and nutrients from the mother’s
body through the placenta.
Throughout
the pregnancy, the fetus obtains food supply and nutrients from the mother’s
body through the placenta.
![]() Food
intake from the placenta by the fetus through the umbilical cord (tali pusat) is called diffusion.
Food
intake from the placenta by the fetus through the umbilical cord (tali pusat) is called diffusion.
-
Pregnant mothers are encouraged to eat food rich in nutrients.
- These are the nutrients required by a pregnant mother and their functions:
|
NUTRIENTS |
FUNCTIONS |
|
Protein |
Assist
in the building of new tissues in the body of the fetus. |
|
Calcium
and Phosphorus |
Important
in the building of strong and healthy teeth and bones. |
|
Iron |
Building
of red blood cells in the blood of the fetus. |
|
Folic
acid |
Strengthens
the defense system of the pregnant mother and her fetus. |
THE IMPORTANCE
OF RESEARCH IN HUMAN REPRODUCTION
1) Human beings face two main reproduction
problems :
a) Sterility or Infertility (mandul),
that is, both husband and wife are unable to reproduce.
b) Birth control, that is, the need
to control the number of children in a family.
2)
Factors of infertility :
a) for male:
- No sperm in semen.
- Low sperm count.
- Low quality of sperm.
-
Impotence (problems with erection of penis).
- Hormone imbalance.
- Infections and diseases.
b) for
females:
- Blocked or abnormally functioning
Fallopian tubes.
- Ovaries that do not produce eggs.
- Abnormal uterus.
- Hormone imbalance.
- Infections and diseases.
TECHNIQUES TO PREVENT STERILITY
1) Surgery:
a) Laparoscope is the technique of using a laparoscope (an
illuminated tubular instrument) to examine the structures inside the abdomen.
2) Artificial insemination:
- this technique is used if the husband is sterile.
- sperm
from a donor male are taken and injected into the uterus of the wife during her
fertile period to induce pregnancy.
- this method increases the chances of fertilization between
the sperm and ovum.
3)
Hormone and drug treatment:
- Clomiphene is
the hormone used by the wife who find it difficult to
ovulate.
- This hormone can stimulate the female to
produce ovum.
- Drugs such as Viagra are used to treat
impotence in men.
4)
Assisted reproductive technologies
(ART):
(a) In Vitro Fertilization
(IVF) - Blocked or abnormal
Fallopian tube.
(b) Gamete Intra-fallopian Transfer
(GIFT) - At least one Fallopian tube is normal. No male fertilization
problem.
(c) Zygote Intra-fallopian Transfer
(ZIFT) - Man has an
infertility problem.
(d) Intra-uterine Insemination (IUI) - Unexplained infertility or certain sperm
problems.
BIRTH
CONTROL TECHNIQUES
1)
Chemical methods :
(a) Contraceptive pills – contain the sex hormone of women which
prevent ovulation by changing the states in the ovary.
BIRTH CONTROL PILLS
(b)
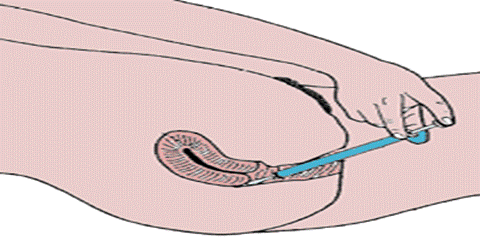
Spermicidal – are
introduced into the wife’s vagina to kill the sperms.
2)
Physical methods :
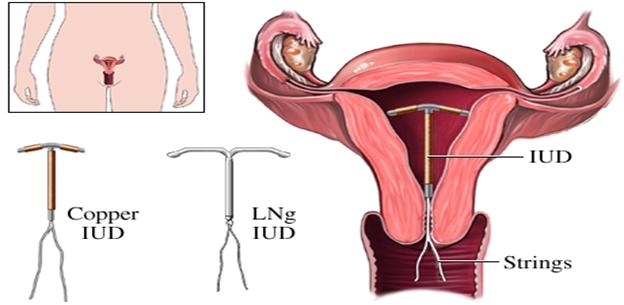
(a) Intra-uterine Device (IUD) – inserted into the uterus can prevent
fertilized ovum from implanting in the uterus and also to prevent sperm
entering the uterus.
(b) Condom – is a rubber sheath pulled over the penis to
prevent sperm from entering the uterus during the ejaculation (pancutan mani).
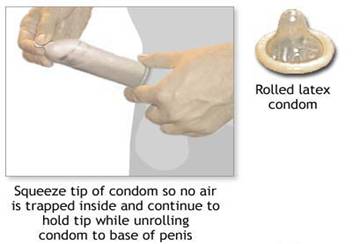
(c) Diaphragm – is a rubber cap
fitted into the cervix of the women to prevent the sperm from entering the
Fallopian tube.
Sterility
(Permanent Methods)
1)
Ligation (Tubectomy) - A process of cutting and tying up both of
the Fallopian tubes of the women so that ovum produced cannot be fertilized by
any sperm.

2)
Vasectomy - A process of
cutting and tying both sperm ducts of the male so that sperm cannot flow
to the penis.
